Energy Storage Cabinet Design Enhancing Efficiency & Safety
Release time:
2025-04-04
Chuntian Technology, a precision manufacturing expert, offers full-process services from design to compliance certification. In new energy storage systems, sheet metal structure design impacts efficiency, safety, and lifecycle costs. Ensure optimal structural integrity for reliable energy storage.
The high-precision machining of medical sheet metal components represents a synthesis of technical capability and management systems, requiring systematic solutions in materials, processes, and quality. As a technology-driven enterprise deeply rooted in precision manufacturing, CTTECH leverages advanced processing equipment, strict quality control systems, and experience collaborating with international medical brands to provide end-to-end services—from blueprint design to compliance certification—helping clients meet the medical industry’s rigorous standards.
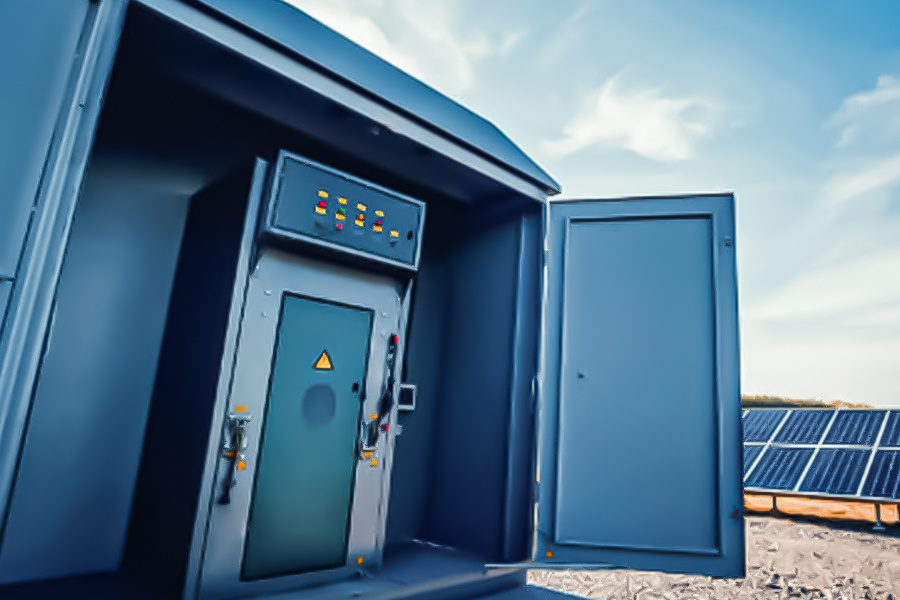
In new energy energy storage systems, the sheet metal structural design of energy storage cabinets, as the carrier for batteries and electrical equipment, directly influences the system’s energy efficiency, safety reliability, and full-life cycle costs. A scientific and reasonable structural design must balance heat dissipation efficiency, protection performance, mechanical strength, and space utilization to provide a foundational guarantee for stable system operation. This article analyzes core optimization strategies for the sheet metal structural design of energy storage cabinets from the perspective of functional requirements, offering professional references for the industry.

Thermal Performance Optimization: Balancing Energy Efficiency and Stability
Heat generated by internal battery packs and power devices in energy storage cabinets can lead to reduced system efficiency or even safety hazards if not effectively dissipated. Sheet metal structural design should enhance heat dissipation capabilities from the following dimensions:
1. Thermal Conduction Path Planning
● Use high thermal conductivity materials (e.g., aluminum alloy, galvanized steel) for the cabinet framework. Integrate heat dissipation fins or flow channels into structural components to shorten the heat transfer path.
● Design independent heat dissipation chambers for key heat-generating components (e.g., battery modules, inverters). Implement cold-hot air zoning through hollow partitions or flow holes to prevent heat accumulation.
2. Aerodynamic Design
● Install symmetrical ventilation holes at the top and bottom of the cabinet, forming natural convection channels with internal guide plates. Alternatively, integrate active heat dissipation devices such as fans or heat pipes, optimizing the structure to reduce air resistance and improve heat dissipation efficiency.
● Adopt modular heat dissipation structures to flexibly adjust solutions according to equipment power consumption, balancing energy efficiency across different operating conditions.
Safety Protection Enhancement: Withstanding Environmental and Mechanical Risks
Energy storage cabinets must operate in complex environments, requiring structural designs that meet strict protection standards (e.g., IP55/IP65) and mechanical strength requirements:
1. Sealing and Corrosion Resistance Design
● Use bent flanges, sealing strips, or welding processes at cabinet joints, combined with waterproof and dustproof rubber rings, to ensure isolation from rain and dust in outdoor environments.
● Apply corrosion-resistant coatings (e.g., epoxy powder coating, galvanized passivation) for surface treatment. For coastal or high-humidity scenarios, optimize sheet thickness or use stainless steel to enhance salt spray resistance.
2. Mechanical Strength and Seismic Design
● Optimize the cabinet framework structure through Finite Element Analysis (FEA), reinforcing key load-bearing parts such as beams and corner columns to ensure impact and vibration resistance during transportation and operation.
● Design anti-loosening structures for battery mounting brackets, paired with shock-absorbing materials, to reduce the impact of vibrations on internal components and ensure connection reliability.

Space and Modular Design: Enhancing System Integration Efficiency
Efficient space utilization and modular architecture are critical directions for energy storage cabinet design:
1. Layered and Zoned Layout
● Physically isolate functional modules (battery compartment, electrical compartment, control compartment) using sheet metal partitions to separate strong and weak currents, reducing electromagnetic interference and improving maintenance accessibility.
● Adopt detachable structural designs with reserved cable channels and equipment installation interfaces, supporting future capacity expansion or equipment replacement to lower maintenance costs.
2. Lightweight and Strength Balance
● Optimize sheet thickness, use hollow profiles, or honeycomb sandwich structures to reduce cabinet weight while meeting strength requirements, minimizing transportation energy consumption and installation load.
● Follow standardized design principles to unify interface dimensions and mounting hole positions, enhancing component interchangeability and production efficiency.
Compliance and Reliability Verification
Structural design optimization relies on a systematic verification system to ensure implementation:
1. Simulation Analysis and Testing
● Use thermal simulation software (e.g., Flotherm) to model temperature distribution under different operating conditions and mechanical simulation to evaluate seismic and wind pressure resistance, proactively identifying design flaws for optimization.
● Finished products must pass IP protection level testing, salt spray testing, vibration and shock testing, etc., to meet industry standards (e.g., GB/T 36276, IEC 62619) and client-specific requirements.
2. Process Feasibility Assessment
● Introduce Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis during the design phase. Optimize structural details (e.g., bending radius, weld position) based on sheet metal processing techniques (bending, welding, spraying) to reduce processing difficulty and manufacturing costs.
The sheet metal structural design of energy storage cabinets is a systematic engineering project integrating functional requirements, environmental adaptability, and processing technology, requiring balance among energy efficiency improvement, safety protection, and space utilization.
Key Words