Sheet Metal Welding: Manual vs. Robotic Differences
Release time:
2025-05-16
Sheet metal welding is the process of connecting metal composite materials by manual or automated equipment arm welding. Manual welding is based on experience and skills, while automated equipment arm welding is based on intelligent control systems and worm gear transmission technology. The two have significant differences in operation methods and principles, and are different in precision, production efficiency, coordination ability, cost expenditure, etc.
Sheet metal welding is a production process that connects metal composite materials by heating or punching. It is widely used in machinery manufacturing, vehicles, aerospace and other industries. In actual production, there are mainly two control methods: manual welding and automatic arm welding. The subject, principle and scope of application of the two are not only related, but also have obvious differences. Manual welding depends on the experience and skills accumulated by the welder, while automatic arm welding depends on the intelligent control system and worm gear transmission technology, forming two different processes of "human-driven" and "technology-driven".
Fundamentally speaking, manual welding is "people-tools-materials" interactive communication. The welder moves the handheld welding machine, operates the molten pool, and welds the parts; automatic arm welding is automatic arm welding "process-robot-welding system" according to the preset welding method and parameters, and the robot is equipped with a welding machine to complete the closed-loop control system. The key differences between the two are reflected in application precision, production efficiency, coordination ability, cost expenditure and other aspects. Enterprises need to choose the standard that suits them according to their needs.
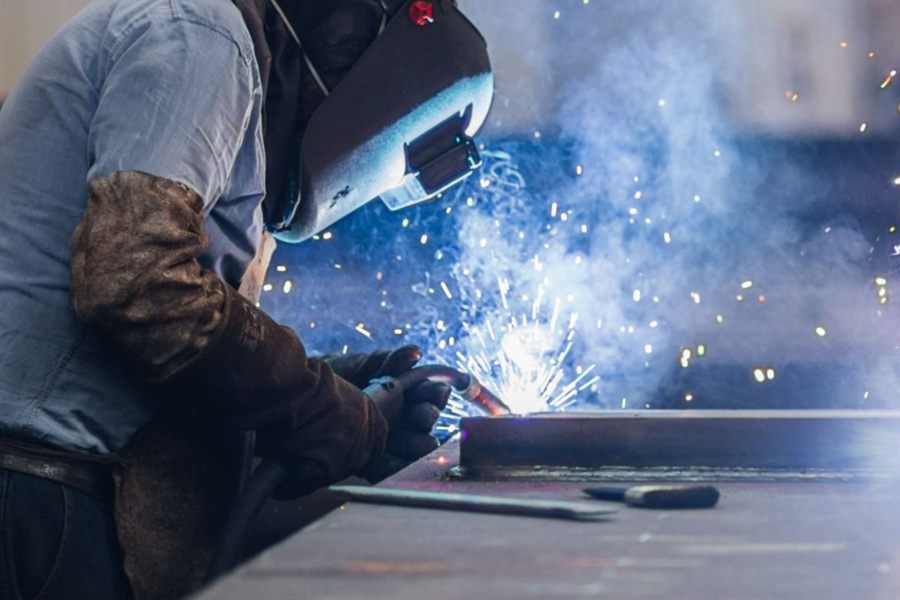

Key differences comparison: multi-level analysis of two welding methods
Operation method and principle difference
Manual welding takes arc welding and argon arc welding as examples. The welder should observe the welding process with the naked eye and control the welding angle, speed and wire feeding amount with the hand muscles. This kind of operation method relies on the "unconscious memory" formed by long-term practice, which will be affected by the welder's fatigue value and emotional state. There are individual differences in the operation accuracy of different welders. The position of the welder needs to be adjusted frequently during the welding process. The adaptability to multiple welding workpieces with complex slopes depends entirely on the welder's on-the-spot judgment.
Automated arm welding is based on industrial robot technology. The robot arm is equipped with a welding machine and connected to an automatic control system. The welding motion trajectory is preset according to CAD drawings or offline programming software. The automatic control system analyzes the coordinate data in real time to drive the robot arm to perform high-precision positioning in three-dimensional space (the repeatability is generally ±0.1mm). Some high-end information systems integrate visual recognition control modules, which can capture the welding position in real time through the camera, dynamically adjust the welding path, and realize the automation of various links such as "cognition-planning-execution".
Precision control and quality reliability
In terms of weld size control, the fluctuation range of manual welding weld width is usually ±0.5mm, while the robot arm welding can keep the fluctuation within ±0.1mm, which is particularly suitable for micro welding (such as ≤1mm width) of precision sheet metal parts. The robot arm avoids the problem of uneven molten pool caused by manual control due to its suction shaking and lack of concentration, and the welding consistency is significantly improved.
Compared with complex workpieces (such as welding the bottom corners of multi-sheet metal bending sheets), manual welding requires frequent adjustments of posture and welding machine posture, which is prone to welding blind spots; the robot arm, with its 6-axis playability, can penetrate into narrow areas that traditional manual labor cannot reach, and cooperate with processes such as shaking welding to achieve consistent operation of all-position welding (vertical welding, overhead welding, flat welding), reducing quality risks such as false welding and false welding.
Efficiency and productivity performance
The daily production capacity of manual welding is subject to the working hours and fatigue cycle of welders. Generally, a single shift (8 hours) can achieve 50-100 pieces of medium-complexity workpieces. Robot arm welding can achieve 24 hours of continuous operation. Through multi-axis linkage or production line integration, the production capacity can reach 3-5 times that of manual labor. In mass production scenarios, the "uninterrupted work" advantage of the robotic arm is particularly obvious, and it is particularly suitable for large-scale electric welding of standardized sheet metal such as automobile covers and distribution boxes.
In terms of modification efficiency, manual electric welding relies on the welder's adaptability to new workpieces. When converting new products, it is necessary to re-understand the welding method, which takes 30-60 minutes; the robotic arm only needs to enable the preset program flow and cooperate with each other to quickly switch the fixture. The modification time can be compressed to within 10 minutes, which significantly improves the flexibility of multi-variety small-batch production.
Cost expenditure and usage scenarios
The initial cost of manual electric welding is low, mainly including basic machinery and equipment such as welding machines and welding machines (the investment of a single equipment is about 10,000 to 30,000 yuan), but it relies on the labor cost of welders for a long time. It is suitable for small-batch production, non-standard product workpieces (such as trial samples, special-shaped parts repair), welding positions that vary and are difficult to program, and small and medium-sized enterprises that are sensitive to equipment investment.
In the early stage of automated arm welding, it is necessary to invest in the robot arm itself (price 100,000-500,000 yuan), welding power supply, positioner, control system, etc. The overall cost is relatively high (single system is about 500,000-1 million yuan), but it can reduce labor costs in the long run (replacing 2-3 welders). It is suitable for large-scale production, high-precision workpieces (such as medical sheet metal, aerospace parts), screens that require 24 hours of continuous operation, and large and medium-sized enterprises pursuing intelligent transformation.
Flexibility and process adaptability
The biggest advantage of manual welding lies in "soft operation". The welder can adjust the welding strategy according to real-time observation. For example, when encountering workpiece size errors, the welding can be performed by manually adjusting the welding machine path. This "on-the-spot decision-making" level is more flexible in the design of non-standard welding (such as curves, spatial heterogeneous welding).
The coordination ability of robotic arm welding is reflected in the "adjustable program". Through the offline programming software, the welding motion trajectory can be quickly changed to meet the requirements of different product workpieces. However, for extremely complex inclined surfaces or unmodeled product workpieces, manual gait analysis or auxiliary positioning is still needed, and the adaptability of the processing technology is subject to the integrity of the digital model.
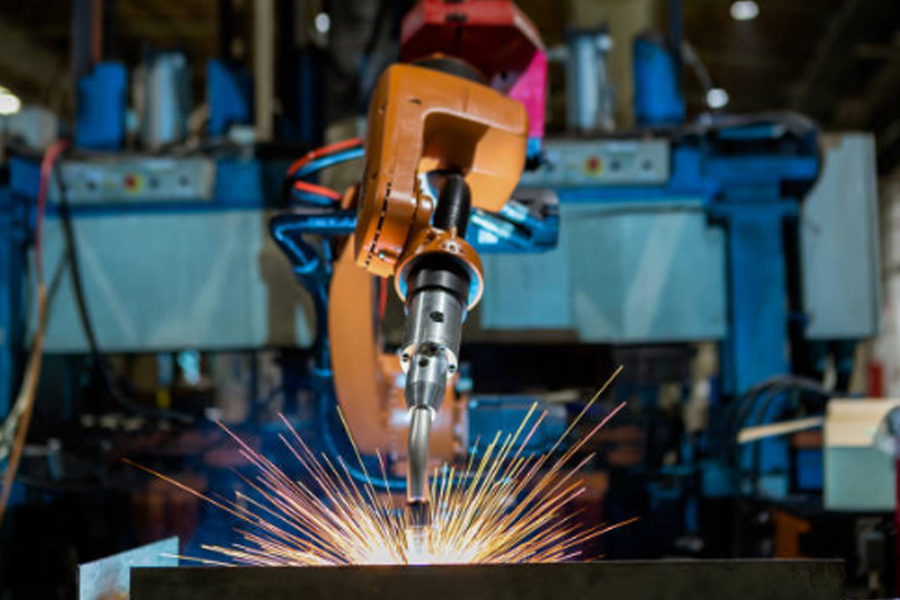

Choose on demand and promote technology and demand matching
There is no absolute good or bad between manual welding and automated equipment arm welding. The key lies in the fit with production needs:
Choose manual welding: suitable for small batch production, non-standardized product workpieces, complex welding positions and difficult programming, and sensitive initial cost scenarios, relying on the experience of welders to complete flexible operations.
Choose robotic arm welding: suitable for large-scale production, high-precision requirements, 24-hour continuous operation, and the pursuit of intelligent transformation. Improve quality stability and production efficiency through big data manipulation.
With the implementation of industrial automation, the application of robotic arm welding in large-scale production will continue to expand, but the soft advantages of manual welding are still irreplaceable. The future development trend of the industry is "human-machine collaboration": the robot arm is responsible for repetitive work, and the human is committed to process improvement and error handling, thus creating a welding production management system with both efficiency and coordination capabilities. Enterprises should rationally select technical specifications based on their actual product characteristics, production plans and cost budgets to maximize the efficiency of sheet metal welding.
Key Words